
From the 3Rs concept created in 1959 to today’s animal welfare acts
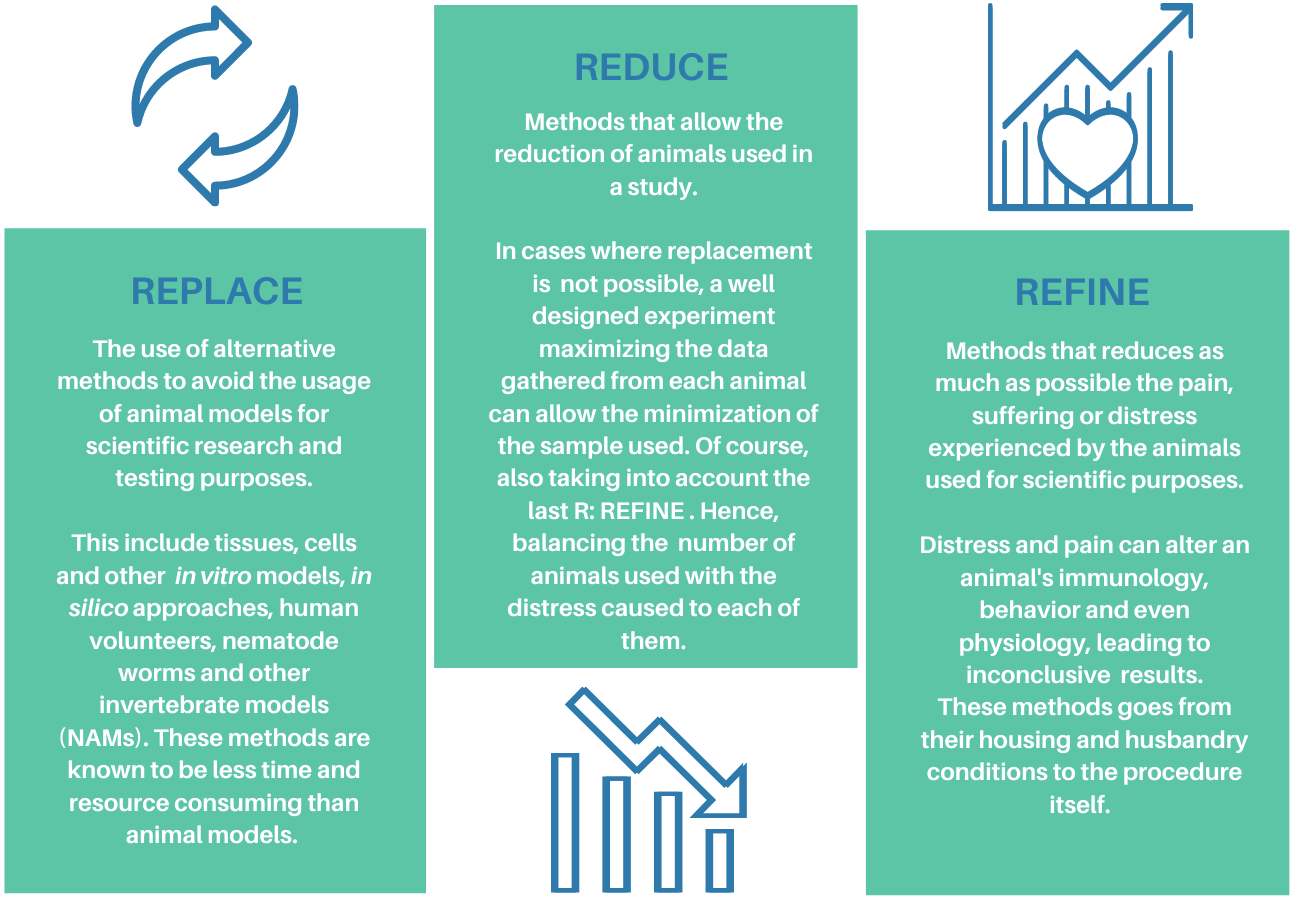
Originally introduced with the aim of making studies with animals more humane, the 3Rs principle (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) is today an entrenched foundation in national and international regulations on animal usage for scientific purposes around the globe.
From Russel & Burch’s concept to today’s redefinition of the 3Rs
In 1959, the scientists William Russel and Rex Burch published The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique where they proposed for the first time the idea of fostering science advancement while preserving the welfare of the laboratory animals. This concept was summarized in the 3Rs principle: Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement.
Nowadays, this concept is integrated in what we call Alternative Testing Methods or NAMs (New Approach Methodologies) and it has become a golden star in the biotech sector due to their cost and resource efficiency solving the current progressive decline in drug discovery efficacy and boosting R&D for unmet medical and consumer needs.
2021 EURL ECVAM – An European Commission status report on alternative animal testing
The 2021 Non-animal Methods in Science and Regulation wrote by the European Commission gather research, development and initiatives that encourage the adoption of non-animal methods for scientific research and studies according to the 3Rs principle, along with the regulations supporting said approaches.
The report include multiple topics such as regulations on toxicity testing related to the usage of NAMs for chemical hazard assessment or the European Commission’s Chemical Strategy for Sustainability as a fundamental pillar for the EU Green Deal. All in all, it englobes the European current status in the adoption of NAMs and the roadmap to fuel their adoption in the next years.
The global Alternative Testing Market is expected to reach a size of $1,78 billion this year (The Business Research Company, 2022) with high growth expectations for the European market fostered by government support initiatives and investment in R&D as described in that report.
The revolution of biological testing – How Nagi Bioscience contributes to the NAMs toolkit
One of the major drawbacks in the usage of alternative testing methods is the lack of standardization and automation, and the protocols for experiments using the nematode C. elegans are not an exception. While C. elegans is a widely recognized biological model among the scientific community for different research applications such as neurodegeneration, aging or toxicity assessment, their experimentation is still largely based on manual work.
With the aim of reducing research pipeline drawbacks and speeding-up R&D processes, Nagi Bioscience developed the innovative Organism-on-Chip technology for scalable, efficient, ethical, sustainable and animal-free substance testing.
After the success of our service projects for highly satisfied customers from diverse industrial sectors, this year’s milestone is about making our product available to the market: The SydLab System for full automated process of culture, treatment, imaging and analysis of C. elegans at an unprecedented throughput and standardization.

Do you want to know more about how Nagi is heading the transition to a new era in biological testing?
Check out our article about alternative testing methods and how Nagi is pioneering the new horizon of the biotech sector.

