
Early Toxicology
Automated early toxicity profiling
toxicity ASSESSMENT HAS NEVER BEEN THAT fast
GET WHOLE-ORGANISM DATA WITHOUT THE USE OF VERTEBRATES.
1 week. 1 experiment.
Toxicity assessment using traditional animal testing can be expensive, time-consuming and subjected to ethical concerns. On the other hand, the use of cell-based models as an alternative for early toxicology tests does not deliver physiological responses and multi-organ crosstalk data.
Bridge the gap between vertebrates and cell models seamlessly with Nagi products. Fast and easy early toxicology assays.

Nagi early Toxicology Assays
REPROductive TOXicology ASSAY
NAGI™ REPROTOX ASSAY
The assay to study the potential effects of your molecules on the reproductive capacity using the model organism C. elegans.
Method Description
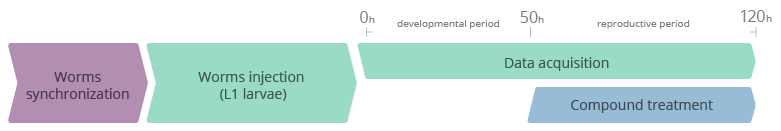
- A synchronized population of C. elegans is automatically injected into the Nagi™ Chips by the SydLab™ One platform at the first larval stage (L1).
- Worms are then automatically confined within dedicated microfluidic chambers inside the Nagi™ Chips and are continuously fed with an E. coli solution (no human intervention needed).
- Worms are chronically and automatically exposed to the test compounds starting from the last larval stage prior to sexual maturity (L4) for 85 hours (day 3 of adulthood). The compounds to be tested are mixed with the E. coli solution. Freeze-dried OP50 E. coli are used as a food source for the whole duration of the experiment, preventing the metabolization of the tested molecules by the bacteria.
- SydLab™ One records images of each microfluidic chamber every hour. Time-resolved phenotypic readouts are then extracted from the collected images thanks to the SydLab™ Analyzer software suite.
Readouts
Maternal effect readouts
- Worm lethality
- Worm size
- Growth dynamics
- Sexual maturity
- Worm shape
Reprotox Readouts
- Fertility
- Embryonic viability
- Progeny accumulation
Check the data
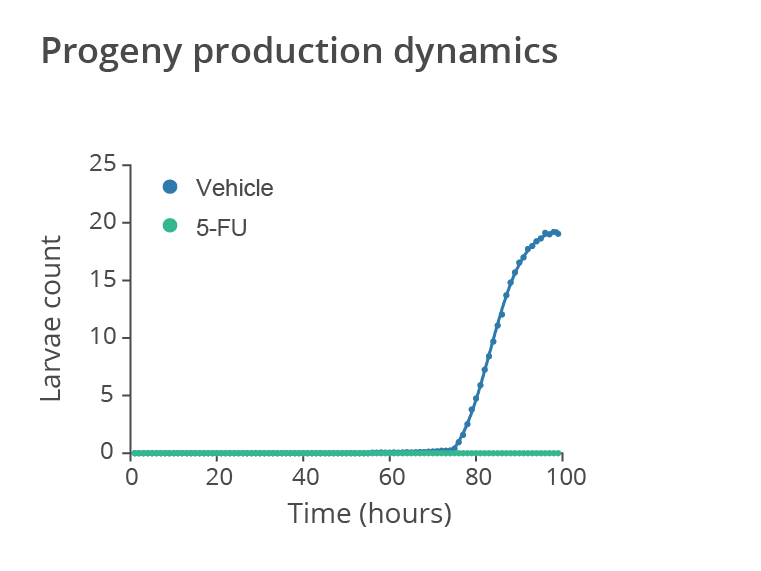
Temporal evolution of the average number of larvae produced by wild-type N2 C. elegans treated with the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) starting from the L4 larval stage vs untreated worms (vehicle). The drug treatment significantly impacts on C.elegans reproductive process. Data provided by SydLab™ One.
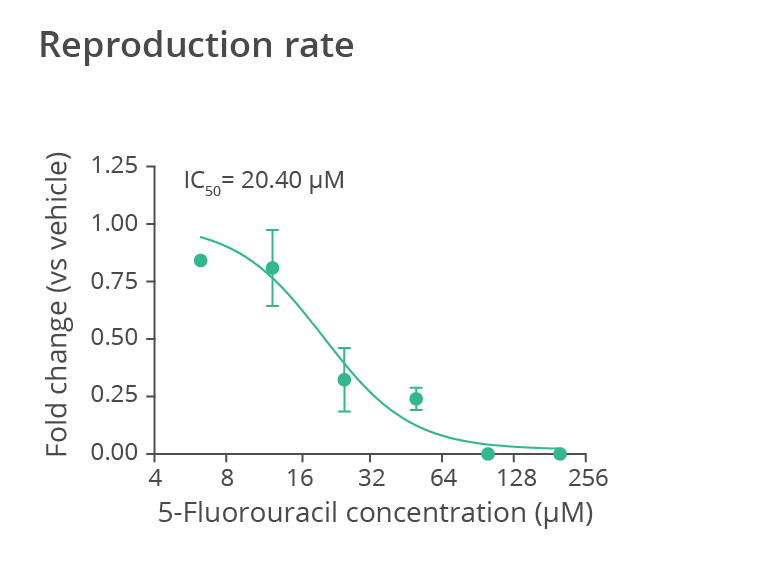
Progeny production rate over the first 24 hours of reproduction for wild-type N2 C. elegans treated with the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) at different doses (data normalized to the value measured for the untreated worm population). 5-fluorouracil treatment specifically affects the worm reproduction, inducing strong embryotoxicity. Data provided by SydLab™ One.
DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY ASSAY
NAGI™ DEVTOX ASSAY
The assay to explore the potential adverse effects of your molecules on the development of C. elegans worms. It can be used as a prediction for teratogenic potency of the test compounds, among other possibilities.
METHOD DESCRIPTION
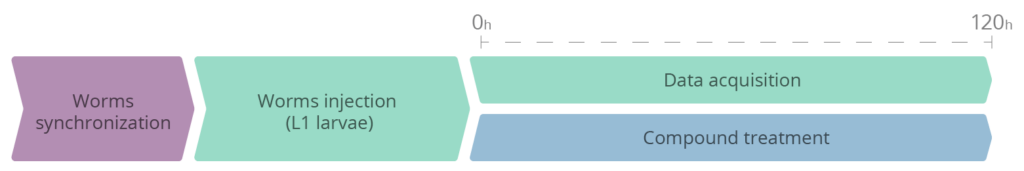
- A synchronized population of C. elegans is automatically injected into the Nagi™ Chips by the SydLab™ One laboratory platform at the first larval stage (L1).
- Worms are then automatically confined within dedicated microfluidic chambers inside the Nagi™ Chips and are continuously fed with an E. coli solution (no human intervention needed).
- Worms are chronically and automatically exposed to the test compounds after the automatized injection (L1 stage) for 130 hours (day 3 of adulthood). The compounds to be tested are mixed with the E. coli solution. Freeze-dried OP50 E. coli are used as a food source for the whole duration of the experiment in order to prevent the metabolization of the tested molecules by the bacteria.
- SydLab™ One records images of each microfluidic chamber every hour. Time-resolved phenotypic readouts are then extracted from the collected images thanks to the SydLab™ Analyzer software suite.
READOUTS
- Worm lethality
- Worm size
- Growth dynamics
- Sexual maturity
- Worm shape
- Fertility
- Embryonic viability
- Progeny accumulation rate
Check the data
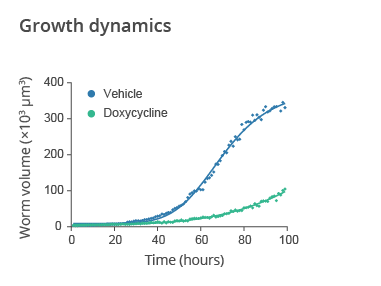
Temporal evolution of the average worm size for wild-type N2 C. elegans treated with the antibiotic doxycycline starting from the L1 larval stage vs untreated worms (vehicle). The drug treatment significantly impacts on C. elegans development, size and growth rate. Data provided by SydLab™ One.
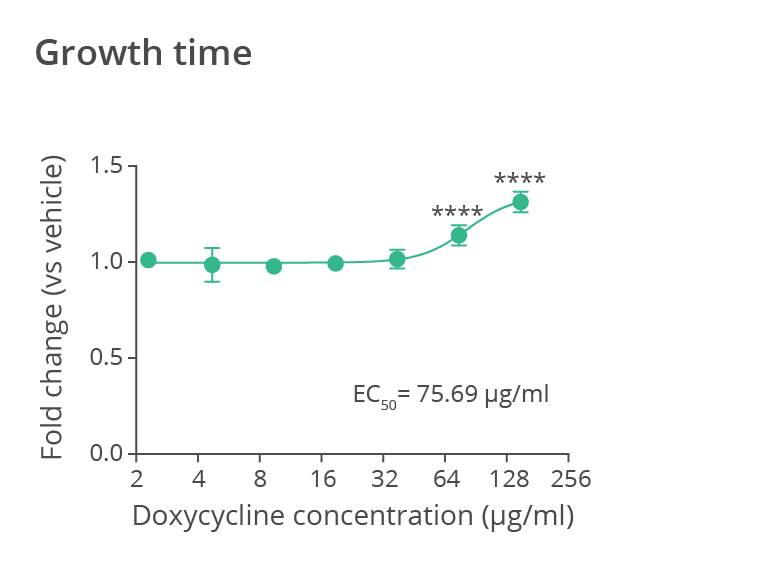
Average time to reach half of the maximal size for wild-type N2 C. elegans treated with the antibiotic doxycycline at different doses (data normalized to the value measured for the untreated worm population). Doxycycline treatment significantly impacts on worm development, resulting in growth retardation and reduced size. Data provided by SydLab™ One.
C. ELEGANS FOR PREDICTIVE TOXICOLOGY
- C. elegans is a well-studied model with useful features for rapid investigations due to its physiological characteristics.
- Many pathways important in development, such as reproduction and modes of toxic action, are conserved.
- Concordant response areas include growth, development, LD50 ranking and neurotoxicity.
Ref: Hunt et al. (US FDA), 2020

“C. elegans can provide a bridge between in vitro assays and mammalian toxicity testing (…), although standardized culture practices are required to achieve consistent results”

LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR BIOLOGICAL MODELS
providing for the first time high STANDARDIZATION & reproducibility levels
to make small organisms toxicology testing easy
-
Failure in later stages of the R&D pipeline is especially costly. We actively pursue technologies to identify adverse toxicology as early as possible, such as Nagi Bioscience’s technologies.

Early Toxicology Safety – Agrochemical Company

Unfavorable toxicological profiles are a major cause of late failure in our discovery pipelines. Failure in later stages of the R&D pipeline is especially costly. We are actively pursuing technologies to identify adverse toxicology as early as possible, including through the use of model systems such as those being investigated by Nagi Bioscience.

Early Toxicology Safety – Agrochemical Company

-
Methodologies to assess lifespan and healthspan measures in a high-throughput manner are currently inadequate in the C. elegans field. The integration of Nagi’s technology opened many possibilities for us as a company.

CEO – Aging Biotech Company

Before proceeding to clinical trials, the efficacy of our existing drugs or combinations thereof for their positive impact on healthspan will be tested in the nematode C.elegans. However, methodologies to assess lifespan and healthspan measures in a high-throughput manner are currently inadequate in the C. elegans field. The integration of Nagi’s technology into Rejuvenate opened many possibilities for us as a company.

CEO – Aging Biotech Company

Nagi Resources: early toxocology
-
Poster
Positioning the “Worm-on-Chip” technology as part of the toolbox for NAMs.
-
Publication
Microfluidic system for Caenorhabditis elegans culture and oxygen consumption rate measurements.
Journal: Lab on a chip
-
Publication
Microfluidic systems for high-throughput and high-content screening using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.
Journal: Lab on a chip
-
Poster
Automated high-content phenotyping of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: application to the toxicity assessment of perovskites.




