What happens when biotechnology, nutrition, and aging science converge? A new era of evidence-driven healthspan begins. Today, we delve into how modern nutritional science, AI, and whole-organism biology are reshaping our understanding of healthy aging.
The concept of healthy aging
has undergone a profound transformation. Once regarded only as a matter of lifestyle and diet, it is now a measurable biological process, governed by conserved molecular pathways that determine resilience, repair, and decline.
The new goal is not just to live longer, but to sustain healthspan, the years of life spent in optimal physiological function.
Behind this shift is a convergence of nutrition, biotechnology, and systems biology, giving rise to a new generation of evidence-based nutraceuticals. These bioactive compounds, often derived from natural sources but studied with pharmaceutical-level rigor, are now being designed to modulate the biology of aging itself.
Central to this revolution is the understanding that the hallmarks of aging are evolutionarily conserved (López-Otín et al., 2023; Ye et al., 2025). This realization has elevated model organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans to essential tools in the nutraceutical pipeline, enabling researchers to observe complex, organism-level effects with translational relevance.
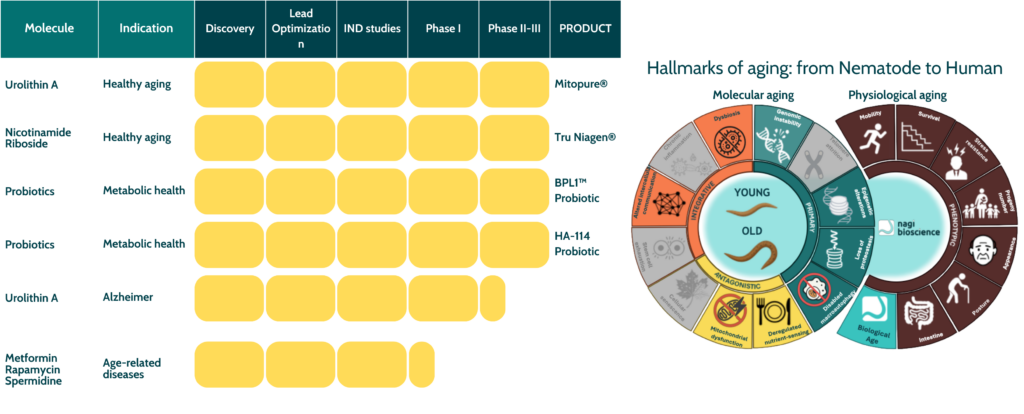
Nutritional science is thus providing mechanistic precision: combining high-throughput phenotyping, AI-driven discovery, and multi-omics integration to uncover interventions that reinforce biological resilience from the cellular to the systemic level.
The Scientific Architecture of Nutraceutical Discovery
Modern nutraceutical development mirrors the pharmaceutical discovery process, but with a distinct emphasis on preserving health rather than treating disease.
It begins with computational modeling and virtual screening, where artificial intelligence platforms predict bioactive compounds likely to influence key pathways of longevity.
From there, promising candidates enter organismal testing pipelines, leveraging species like C. elegans for rapid, whole-body evaluation of compound efficacy. These models, whose genomes share significant overlap with humans, offer a powerful lens through which to assess both safety and function (Ye et al., 2025).
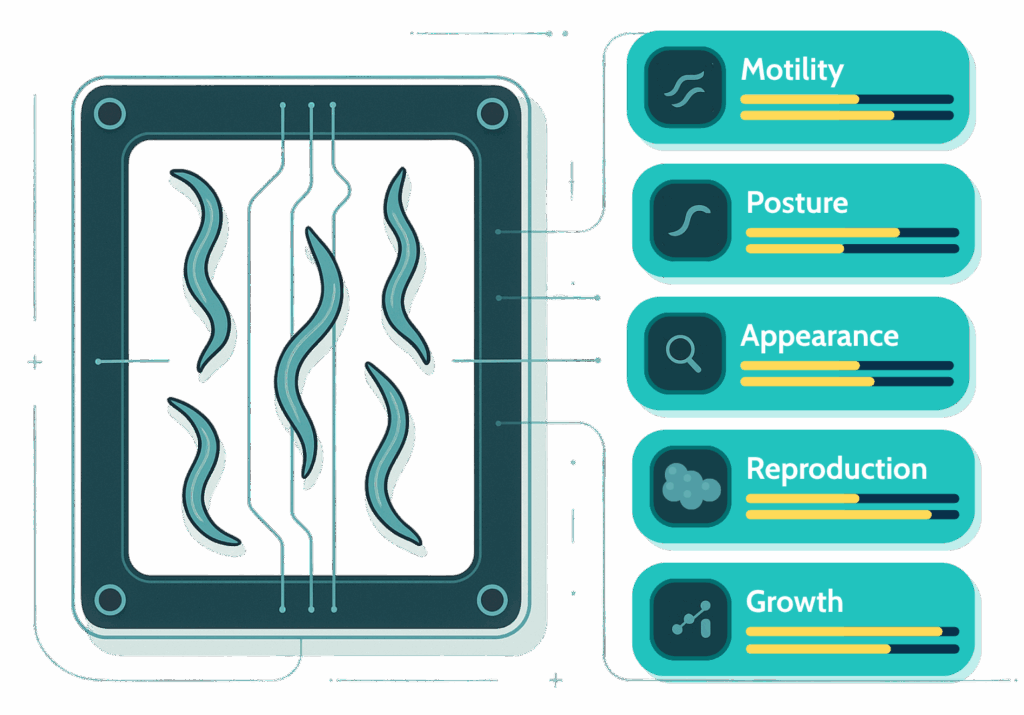
Today’s most advanced platforms measure a suite of physiological parameters like biological age, lifespan, motility, growth, and reproduction, simultaneously. This multidimensional approach captures both how long an organism lives and how well it functions.
This iterative cycle “predict, test, validate” has become the blueprint for credible nutraceutical science.
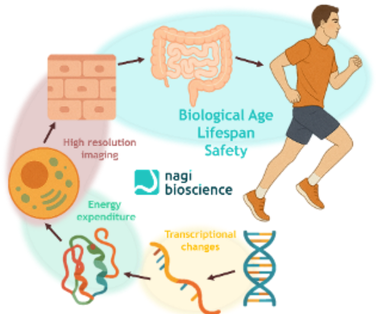
Subsequent layers of molecular and transcriptomic analysis link these phenotypic shifts to underlying mechanisms: improvements in mitochondrial respiration, enhanced autophagy, or reduced inflammatory signaling (Jacquier et al., 2024). Finally, human trials validate the most promising compounds through measurable biomarkers for aging signatures (Silva et al., 2023).
Translating Discovery into Meaningful Mechanisms
The power of this approach lies in establishing mechanistic causality. Nutraceuticals no longer rely on claims of potential mechanisms or subjective well-being; they demonstrate quantifiable modulation of biological processes known to drive aging.
One of the best examples is Urolithin A, a gut microbiome–derived metabolite that promotes mitochondrial renewal through mitophagy (Ryu et al., 2016; Kuerec et al., 2024).
Preclinical studies in C. elegans and rodents revealed improved endurance and muscle strength, findings then replicated in human trials (Wang et al., 2025).
Similarly, Nicotinamide Riboside, a vitamin B₃ derivative, restores NAD⁺ metabolism and enhances energy homeostasis — mechanisms central to maintaining cellular resilience (Mouchiroud et al., 2013; Ristori et al., 2025).

These cases illustrate a recurring pattern: compounds identified in model organisms advance through layered validation until their molecular effects align with measurable, organism-level benefits.
To bridge this continuum, researchers increasingly use phenotypic aging clocks, such as those based on whole-organism behavior. These tools provide dynamic readouts of biological age, a synthetic index integrating neuromuscular, metabolic, and stress-response functions.
In this context, phenotypic clocks do not replace molecular biomarkers, they contextualize them, allowing scientists to determine whether a compound’s molecular impact translates into tangible functional gains.
B-Age fills a key gap by serving as a high-throughput, whole-organism platform to validate compounds, pre/pro/postbiotics, and other ingredients. It doesn’t just measure biological age; it separates it into 5 Vital Traits, offering a detailed health profile. Combined, these tools allow us to explore a wider chemical landscape and speed up the identification of nutraceuticals that deliver genuine healthspan benefits in living organisms, not only in cell-based assays.
Nicotinamide (NAM)
NAM, a precursor of NAD⁺ involved in metabolism, DNA repair, and longevity signaling, demonstrated a clear anti-aging effect at day 10 at its highest concentration, with an overall reduction in biological age. Vital trait analysis showed pronounced benefits in Reproduction and Posture suggesting NAM’s broad impact on cellular maintenance.
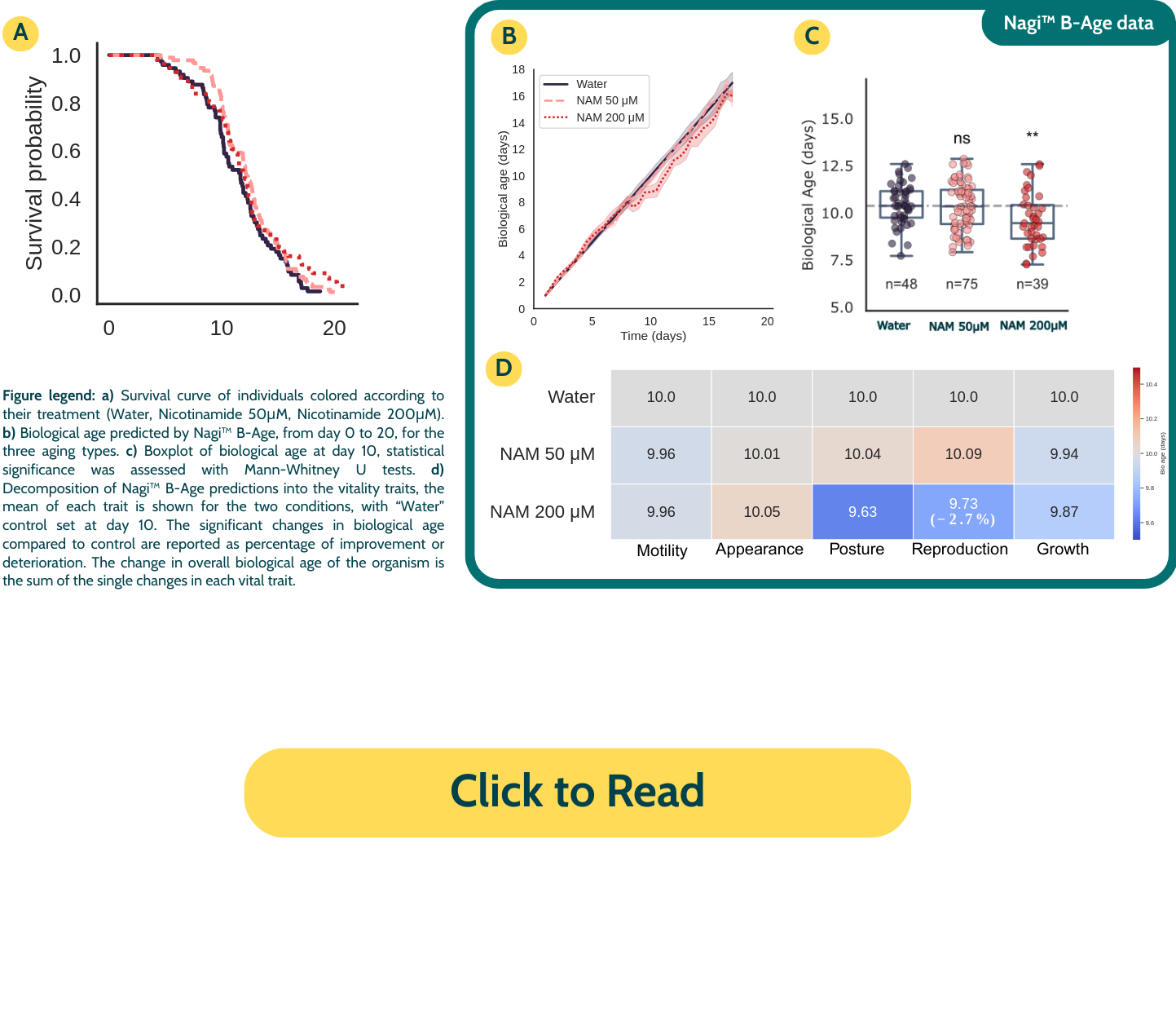
Metformin
Metformin, known for its anti-aging activity through enhanced mitochondrial recycling, significantly reduced biological age starting from day 7, with a clear dose-dependent effect observed by day 10. Notably, the Motility trait improved substantially (up to 4.4% improvement compared to control), consistent with metformin’s role in supporting mitochondrial function and muscle health.
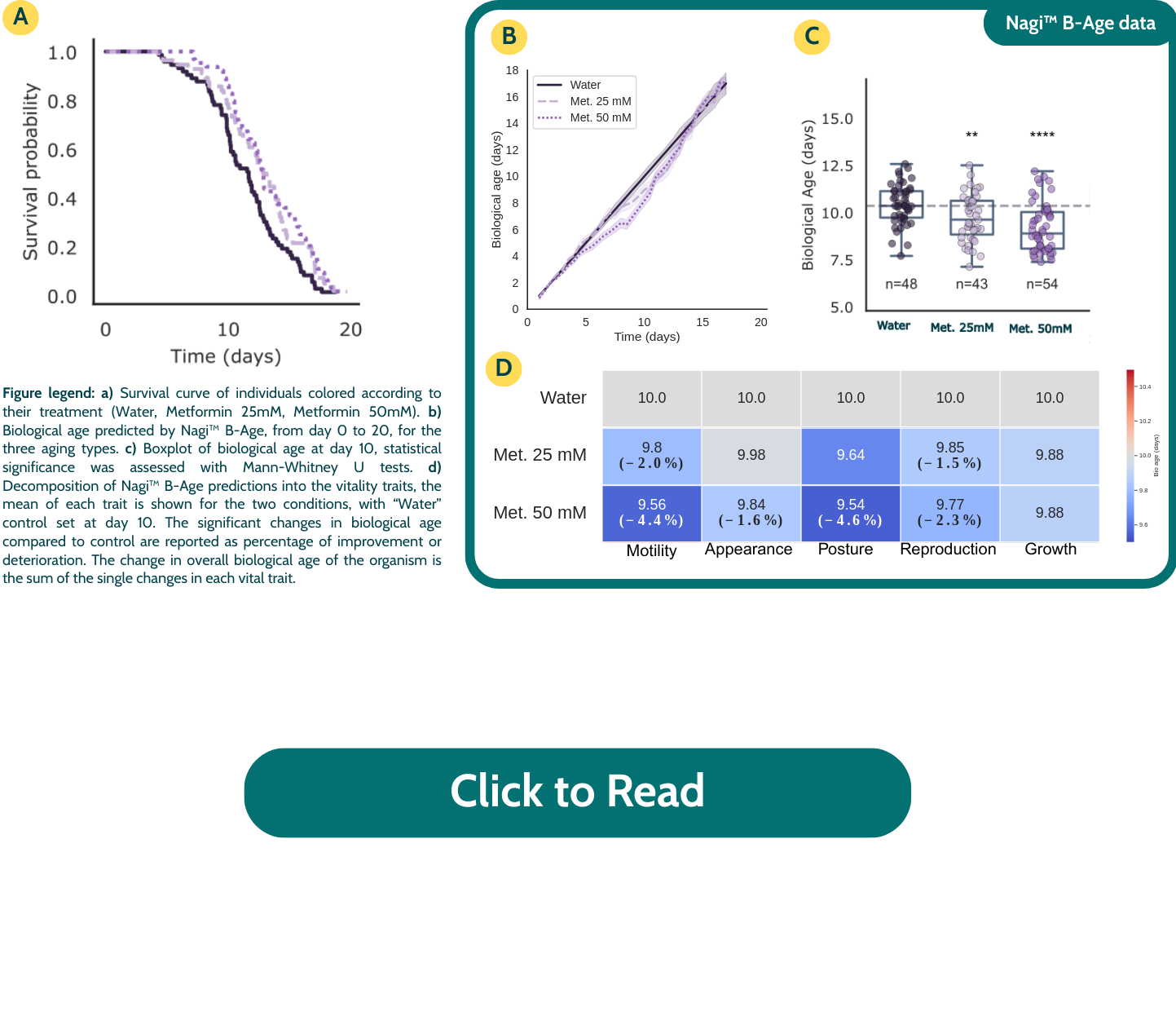
From Evidence to Integration: Tools for Translational Validation
Despite the abundance of molecular data, translating mechanistic insight into meaningful functional benefit remains one of the greatest challenges in nutraceutical science. A compound may alter gene expression or metabolite profiles without necessarily improving endurance, stress resilience, or cognitive health.
Whole-organism phenotyping and AI-enhanced biological clocks address this challenge by connecting molecular cause with physiological consequence. These systems, trained on high-dimensional behavioral data, continuously predict biological age and health outcomes in living organisms.
This integrative approach allows for early, cost-efficient screening of compounds, reducing reliance on long-term clinical trials while retaining translational value. Moreover, by capturing systemic interactions between muscles, neurons, and metabolism, these assays help identify compounds that promote whole-body homeostasis rather than isolated pathway effects.
When combined with AI discovery platforms, such systems form a closed feedback loop: computational models generate predictions, organismal tests validate them, and results refine the algorithms. This synergy is redefining how we identify and de-risk the next generation of geroprotective bioactives.

CLOSING REFLECTIONS
From Bench to Biological Resilience
The nutraceutical field is central to the science of aging, it is one of its most dynamic frontiers. The tools to measure, predict, and validate are in place; what remains is integration across disciplines.
The insights from global conferences underscore how rapidly this integration is unfolding, spanning molecular mechanisms, preclinical screening, and human validation.
Ultimately, the future of healthy aging depends on our ability to connect the molecule to the mechanism, and the mechanism to measurable function. The path forward is both scientific and human: translating discovery into resilience, and data into longer, stronger, more meaningful years of life.

